Causes and Treatment of Atherosclerosis and Arterial Narrowing
Atherosclerosis is a disease of the arteries, and arterial narrowing (stenosis) is the most severe consequence of atherosclerosis. Some regard atherosclerosis as part of aging, but lifestyle—and especially diet—clearly plays a major role. Therefore, with the right lifestyle the arterial narrowing may be improved. What is atherosclerosis? The arteries (arterial vessels) are responsible for carrying oxygen-rich blood […]
Atherosclerosis is a disease of the arteries, and arterial narrowing (stenosis) is the most severe consequence of atherosclerosis. Some consider atherosclerosis to be associated with aging, but it is certain that lifestyle—and particularly diet—plays a significant role. From this it follows that with an appropriate lifestyle arterial narrowing can potentially be improved.
What is atherosclerosis?
The arteries are responsible for transporting oxygen-rich blood from your heart to the rest of your body. A healthy artery has a strong, elastic structure and pulses. With each heartbeat it expands (to accommodate the blood pumped by the heart) and then returns to its original diameter.
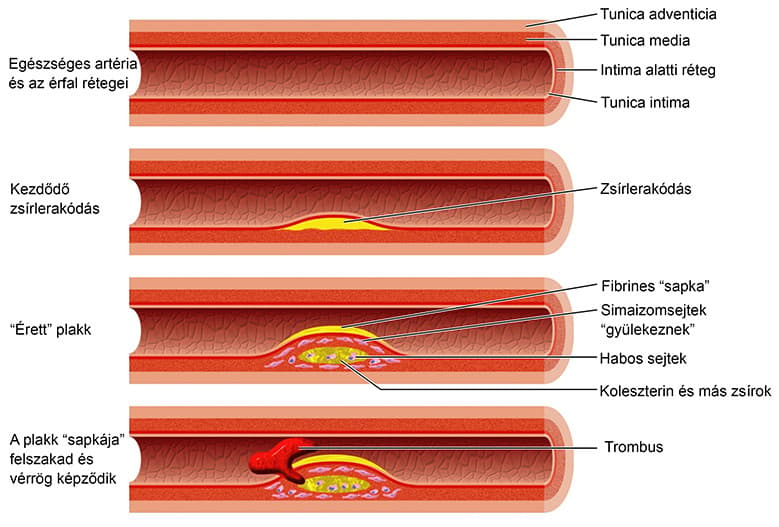
Atherosclerosis is an unfavorable process because this elasticity of the arterial wall is lost. If it cannot dilate, the same amount of blood can only pass through at a higher pressure, and never more. This can have two important consequences. First, blood pressure increases, leading to hypertension. Second, when needed the artery cannot deliver enough blood to an area, resulting in ischemia, i.e., impaired blood and oxygen supply.
Atherosclerosis is the underlying problem that can lead to various diseases and severe conditions. These include high blood pressure, stroke, heart attack, peripheral arterial disease, and even dementia and cognitive decline.
What is arterial narrowing (stenosis)?
A stiff arterial wall alone is already harmful because it leads to high blood pressure. In rigid arteries the blood flows faster, which results in impaired tissue oxygenation. This can remain symptom-free at rest for a long time, but if demand increases (e.g., due to physical work), oxygen deficiency will present as significant symptoms (for example, tight chest pain, neurological symptoms from cerebral circulation disturbance, calf cramps and pain).
I described the process of arterial narrowing in detail in this article, read it here: High cholesterol level – useful information
The following illustration shows the steps in the development of arterial narrowing.
Symptoms of arterial narrowing
Arterial narrowing does not occur in only one artery at a single localized point; it affects all the arteries in your body. But it does not affect them all equally. In some places it can be more severe, and therefore the first signs of arterial narrowing will appear where the deposits are thickest and the artery is narrowed to such an degree that it already causes circulatory disturbance in the area supplied by that vessel. Because different arteries supply blood to the brain, heart, organs, limbs and muscles, the symptoms of arterial narrowing are correspondingly varied.
Carotid artery occlusion
If atherosclerosis is strongest in the arteries that supply the brain, ischemia will first develop there. Some brain regions do not receive sufficient blood and the neurons receive too little oxygen. This is an ischemic stroke (formerly called apoplexy), whose symptoms include sudden weakness, confusion, severe headache, loss of consciousness, blurred vision, speech disturbances, paralysis, gait disturbance, dizziness, unexplained falls, and loss of coordination or balance. The outcomes depend on the type of occlusion. With partial or temporary occlusion the stroke can be reversible and symptoms may completely disappear. With severe or complete occlusion stroke carries significant mortality, and survivors often live with residual deficits (paralysis, speech impairment, inability to live independently, etc.).
Coronary artery occlusion
The heart muscle is very sensitive to impaired blood supply; if the coronary arteries are the most affected by atherosclerosis, cardiac symptoms appear first. Partial occlusion causes constricting chest pain (medically called angina pectoris), which can radiate to the upper arm, back and neck. Other symptoms include sweating and shortness of breath. Angina pectoris can sometimes be felt in the upper abdomen under the ribs and may be mistaken for a stomach problem. Important to know: sudden emotional stress often triggers angina-like symptoms that are not related to atherosclerosis.
Chest tightness is only the "entrance"! Complete occlusion of a coronary artery is a myocardial infarction (heart attack). Heart muscle cells die from lack of blood and oxygen, which leads to permanent loss of cardiac function and often immediate death.
Occlusion of peripheral arteries (peripheral arterial disease)
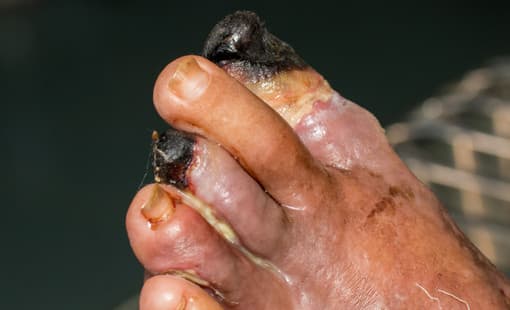
It often happens that the first symptoms appear in your legs. In everyday language this is called arterial narrowing; the medical term is peripheral arterial disease (PAD). Although the symptoms are strongest in the legs, remember that atherosclerosis is present elsewhere in the body as well. A leg affected by arterial narrowing feels cold to the touch and looks pale. The first symptom is sudden calf pain during walking that forces the patient to stop. On rest it disappears within 1–2 minutes, but after a certain walking distance it reappears. The pain is caused by inadequate oxygen supply to the muscles. In severe cases tissues (primarily the toes) become blackened and die. Dead tissue must be removed, which leads to amputation. Hungary ranks among the highest in the world in the number of amputations per capita. Relative to population size, the most amputations occur here.
In developed countries, including ours, cardiovascular diseases top the mortality statistics, claiming nearly 100,000 lives annually. A large proportion of cases are entirely asymptomatic. Often the first sign is a heart attack or stroke, which—even if survived—can leave significant long-term deficits.
Occurrence of arterial narrowing
Arterial narrowing can remain symptom-free for many years—often you only notice it when the problem is already more serious. The likelihood of arterial narrowing increases with age, but it is advisable to pay attention to the signs even in your thirties, because early treatment is important to prevent potential consequences.
The risk of arterial narrowing is high if
- you have diabetes,
- you smoke,
- you are overweight,
- you suffer from high blood pressure,
- your cholesterol level is high, and
- there is a family history of the condition.
Additional risk factors include:
- living a stressful life,
- being in menopause (for women),
- having other heart diseases,
- experiencing memory problems,
- a previous heart attack or stroke.
Prevention of atherosclerosis
Renovating damaged arteries is much, much harder than preventing the damage. This is only possible through a lifelong healthy lifestyle!
- Pay attention to healthy eating. Reduce carbohydrate intake! The culprit is not cholesterol, but excessive sugar! A predominantly plant-based diet may be appropriate.
- Ensure adequate antioxidant intake.
- Reduce stress!
- Exercise regularly and reach an optimal body weight.
- Quit smoking and other harmful addictions.
Treatment of arterial narrowing
You cannot wait for others when it comes to arterial narrowing! There is no truly effective cure—only symptomatic treatments are available.
You alone can slow the progression of the disease by radically changing your lifestyle.
- It is not too late to change your lifestyle! Quit smoking.
- Ask a nutrition specialist to help set up a low-carbohydrate diet that promotes mitochondrial health.
- The best remedy is exercise that thoroughly works the leg muscles (walking, cycling). This is essential for maintaining vascular health!
- Your doctors will prescribe vasodilators and circulation-improving medications.
- The so-called mofetta baths exploit the vasodilating effect of carbon dioxide.
- BEMER therapy can improve microcirculation.
- Magnetic therapy devices help by accelerating regenerative processes and, to a lesser extent, improving microcirculation. Their circulation-improving effect is less than that of BEMER, but they are less expensive.
- With a muscle stimulation device you can effectively improve blood circulation in the legs and delay deterioration of the condition.
When to use a device?
The best way to prevent arterial narrowing is healthy eating and regular exercise! Even when the first symptoms of arterial narrowing appear, it is not too late. Thoroughly exercising the calf muscles—that is, daily walking, jogging or cycling for at least 40–50 minutes—is the best remedy. And of course, the diet.
You need a device if, despite warning symptoms, you have not changed your lifestyle. In that case the disease reaches a stage where you cannot move even if you wanted to.
Advanced arterial narrowing does not even allow walking. Little fresh blood reaches your leg muscles and during walking the muscles become oxygen-deficient, causing such intense calf pain that you cannot take another step. In the past this disease was called the "window-shopping disease." After a few hundred steps you must rest for a few minutes, during which—because there is nothing else to do—you might look around.
So, if you have allowed it to reach this point, you must prevent tissue death and the gradual amputation of your foot.
At that stage, only technological devices remain as an option.
Muscle stimulation in reducing symptoms of arterial narrowing
Attention! Persons with a pacemaker must not use such a device.
The self-adhesive electrodes of the muscle stimulator device are attached to the calf muscles (or possibly to the thigh as well) and through them the device generates a series of muscle contractions in your calf. The treatment essentially replaces walking or cycling (since pain may prevent you from doing those activities).
The rhythmic contractions of the muscles (induced by the device) improve blood circulation, warm the cold limb, and reduce pain. It is particularly effective in preventing nocturnal calf cramps!
It also speeds up the healing of hard-to-heal wounds (ulcers). After vascular surgery it shortens recovery time and helps protect vascular grafts.
If your complaints no longer allow regular daily exercise, then use a muscle stimulation device on your lower leg muscles once or twice daily, or if necessary up to three times a day.
The Elite SII device can be an appropriate choice.