Sinusitis
Sinusitis (also known as paranasal sinus inflammation) is a viral or bacterial infection of the cavities located in the bones of the facial skull. Without treatment, sinusitis can develop into a severe condition — chronic rhinosinusitis — which may even require surgical intervention. With appropriate treatment, however, most sinus infections heal well.
Causes of sinusitis
The paranasal sinuses in the facial skull are essentially air-filled sacs whose walls are lined with ciliated glandular epithelium. The cilia "beat" in a way that moves dust, pathogens and other material trapped on the mucous membrane toward the nasal cavity. If this cleaning mechanism is obstructed for any reason, it can lead to sinusitis. Such causes may include substances that trigger mucosal swelling: pollen, dust and pathogens. The mucosa swells, debris cannot drain from the sinuses, and inflammation develops.
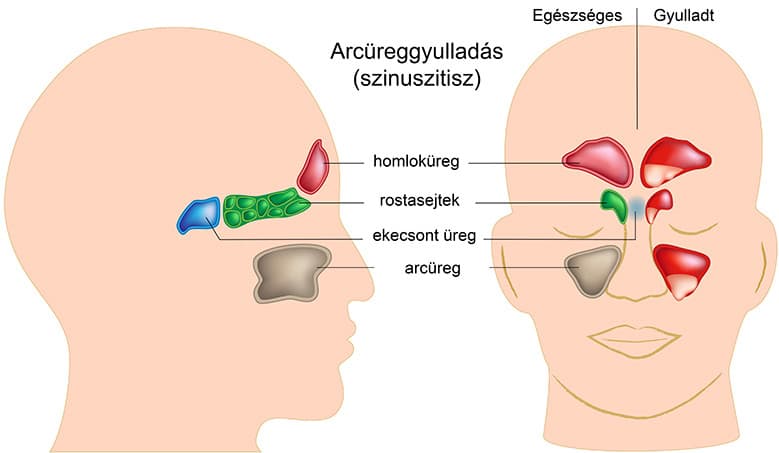
The following sinuses may be affected:
- the frontal sinus (sinus frontalis), located above the eyes in the frontal bone
- the maxillary sinus (sinus maxillaris), located within the cheekbones behind the zygomatic bones
- the ethmoidal air cells (sinus ethmoidalis), located between the eyes behind the nasal bridge
- the sphenoidal sinus (sinus sphenoidalis), located deep behind the ethmoidal cells
Symptoms of sinusitis
The paranasal sinuses have several functions: they warm incoming air and help shape various sounds. If infection or inflammation occurs in the sinuses and this condition lasts less than four weeks, it is called acute sinusitis. If acute sinusitis becomes persistent and the symptoms last longer than three months, it develops into chronic sinusitis.
The most common symptoms of sinusitis: nasal pain, nasal congestion, sneezing, high fever, headache (worsens when bending forward) and thick nasal discharge that is green, yellow or blood-tinged.
Risk factors for sinusitis: allergic rhinitis or hay fever, asthma, smoking, weakened immune system, cystic fibrosis, nasal polyps, congenital nasal abnormalities.
Treatment of sinusitis
Prescription medications, such as nasal drops, nasal sprays or antibiotics, are the most commonly used treatments. They often only provide temporary relief and, unfortunately, may have side effects.
If symptoms do not resolve with medication, the only treatment is surgical opening of the cavities so that the secretions can drain and the cleaning and healing process can begin.
Among natural remedies, salt therapy can be used. The main effect of salt is to loosen mucus. This helps liquefy and clear the secretions. The SaltDome salt therapy device can be an appropriate choice.
Product recommendation: SaltDome salt therapy device
If you want to generate the beneficial salty air in the comfort of your home, choose the SaltDome ultrasonic salt therapy device. Read customer reviews to learn about users' experiences!



